Mexico: With the United States in its left hand and China in its right, it is an unavoidable springboard in Latin America
Publish Time:2025-11-21 09:29:57Pageviews:123


abstract: It is the only country in Latin America with a complete range of industrial categories, but its exports to the United States account for 82% of its total exports. Meanwhile, China is its second largest source of imports.
When it comes to Mexico, do you still have the stereotypical impression of "tequila, drugs, tacos, cacti"?
In fact, as the second-largest economy in Latin America, Mexico's per capita GDP soared to $13,900 in 2024, even surpassing that of China.
Its online retail market revenue reached 39.1 billion US dollars, with a growth of over 300% in five years, topping the world.
It is the only country in Latin America with a complete range of industrial categories, but its exports to the United States account for 82% of its total exports. Meanwhile, China is its second largest source of imports.
It can be said that under the competition among major powers, Mexico is rising to become a key hub on the global trade map.
In this article, the Yiwu Index takes you to Mexico.

Image source of Mexico City Cathedral: Internet
01
Mexico: From a regional power to an economic powerhouse
(1) Location advantage: A global trade gateway connecting North and South America
Mexico has a land area of approximately 1.964 million square kilometers, ranking 14th in the world and 3rd in Latin America. The coastline is 9,330 kilometers long and it has more than 20 important ports.
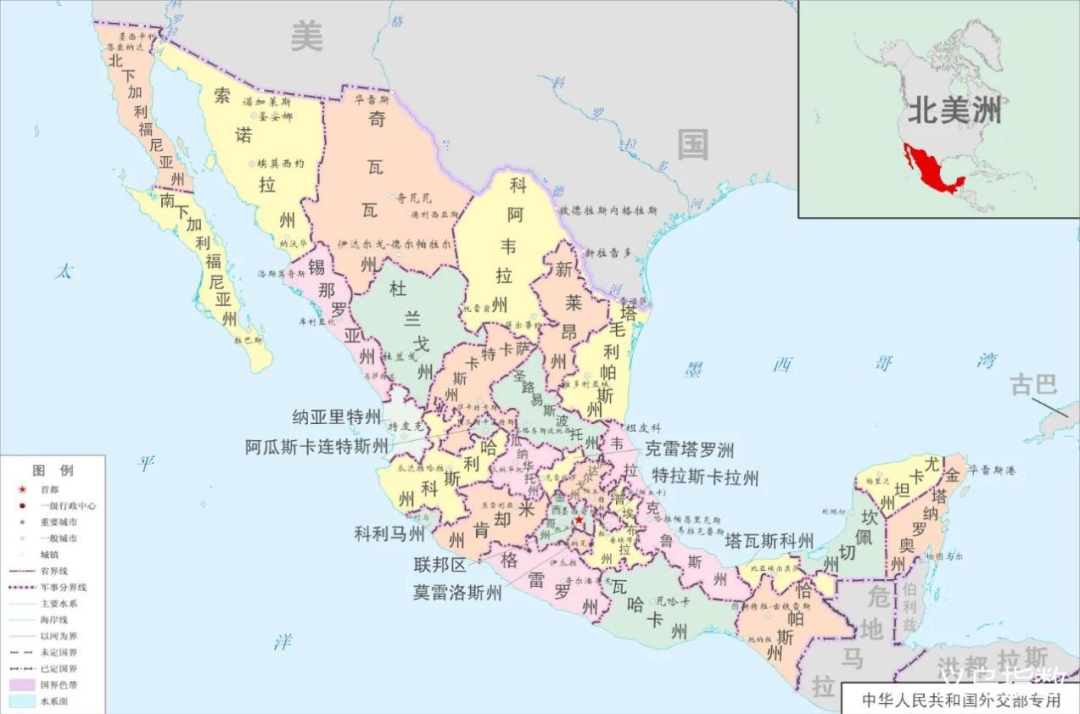
Map of Mexico Source: Internet
Mexico enjoys a superior geographical location: it borders the United States to the north, Guatemala and Belize to the south, the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It seamlessly connects North and South America and radiates to Europe, Asia, Africa and Oceania, serving as a natural gateway for global trade and investment flows.
(2) Population structure: Young age, highly urbanized, and strong consumption
In 2024, Mexico will have a population of 130 million, ranking as the tenth most populous country in the world, with a population growth rate of 0.9%.
The population is getting younger: The median age of the Mexican population is 26 years old, which is much younger than 38.5 years old in China. Among them, the proportion of the working population aged 15 to 64 is 64%.
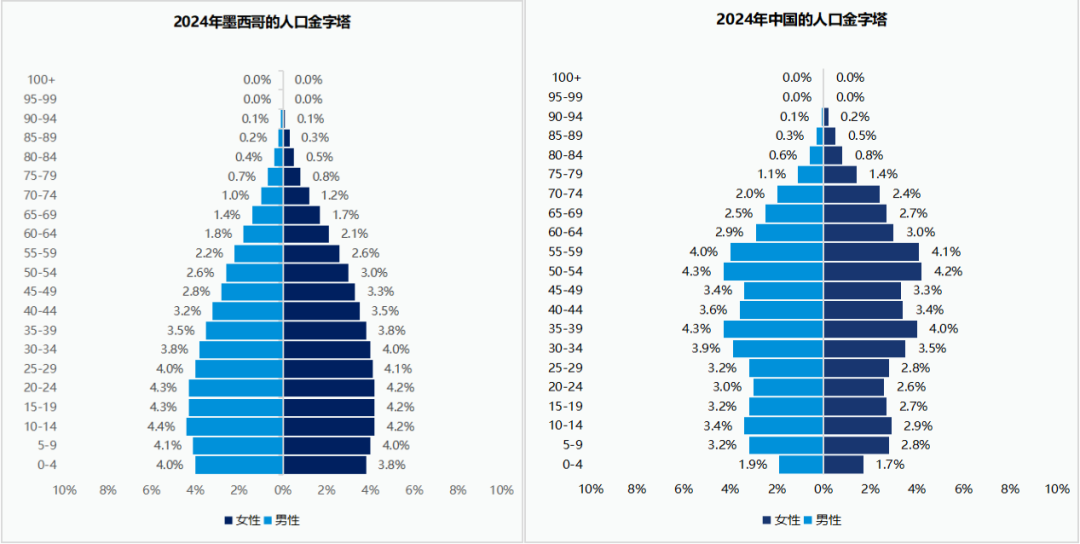
Data source: populationpyramid
www.ywindex.com
The urbanization process is remarkable: In 2024, Mexico's urbanization rate will reach 88%, far exceeding China's 67%. A large number of people are concentrated in major cities such as Mexico City, Monterrey and Guadalajara.
Low savings rate and a preference for advanced consumption: Mexicans generally advocate "living for the moment" and tend to consume in installments. According to the data monitoring of Yiwu Index, the average savings rate of Mexicans will be less than 18% in 2024. The strong willingness to consume and the habit of not saving are conducive to the development of the small commodity industry. In 2024, Mexico's personal consumption as a proportion of its GDP will remain at a high level of 70.26%, even higher than that of the world's largest consumer, the United States (68.9%).
Driven by multiple factors such as "young population + urban concentration + strong consumption willingness", e-commerce has experienced explosive growth directly: in 2024, the revenue of Mexico's online retail market reached 789.7 billion pesos (about 39.1 billion US dollars), increasing by approximately 20% year-on-year and over 300% compared to 2019, with an average annual growth rate of 33%, far exceeding the global average of 25%.
Mexican online retail market revenue from 2019 to 2024 (Unit: billion pesos)
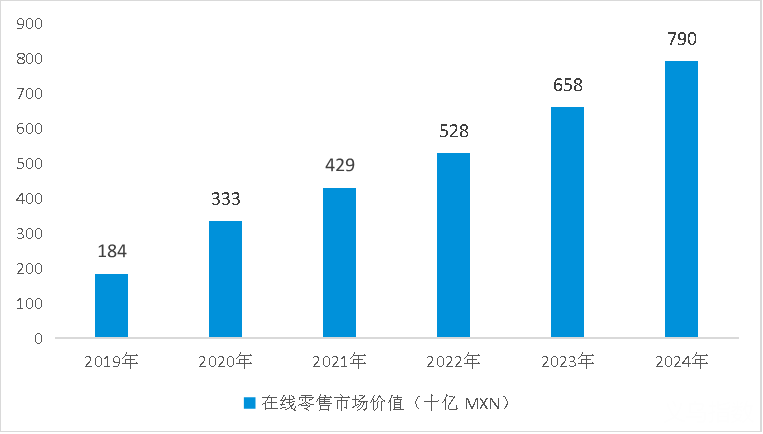
Data source: AMVO
www.ywindex.com
(3) Economic development: The only country in Latin America with a complete range of industrial categories
Mexico is the second-largest economy in Latin America, with a GDP of 1.85 trillion US dollars in 2024, second only to Brazil and ranking thirteenth globally. This year, the "Railway-Road-Infrastructure" plan was launched, with an investment of nearly 100 billion US dollars to comprehensively promote the construction of key infrastructure such as railways, highways, energy and communications, aiming to unleash growth potential.
The main economic data of Mexico are as follows:
Gross domestic product (2024) : approximately 1.85 trillion US dollars
Economic growth rate (2024) : 1.5%
Per capita GDP(2024) : 13,900 US dollars
Mexico's GDP from 2020 to 2024 (Unit: billion US dollars)
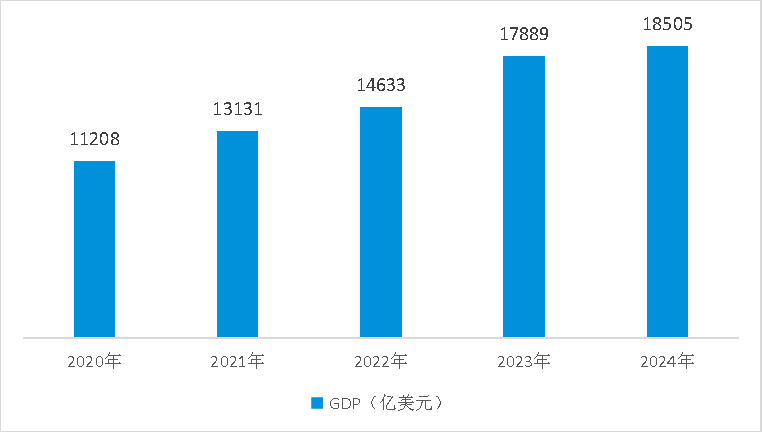
Data sources: World Bank, Yiwu Index
www.ywindex.com
Mexico is known as "the only country in Latin America with a complete range of industrial categories", covering multiple fields such as petrochemicals, power, mining, metallurgy and manufacturing. The industrial sector is the core of the national economy, absorbing over 30% of the employed population. Among them, the manufacturing industry holds a pillar position, contributing approximately one quarter of the country's GDP and over 75% of its export earnings. The automotive industry stands out particularly and is the largest sector in manufacturing. Mexico is the world's seventh-largest producer of passenger vehicles and the fourth-largest producer of auto parts. 70% of its car production is directly supplied to the US market, meaning that for every ten cars produced in Mexico, seven are exported to the United States.
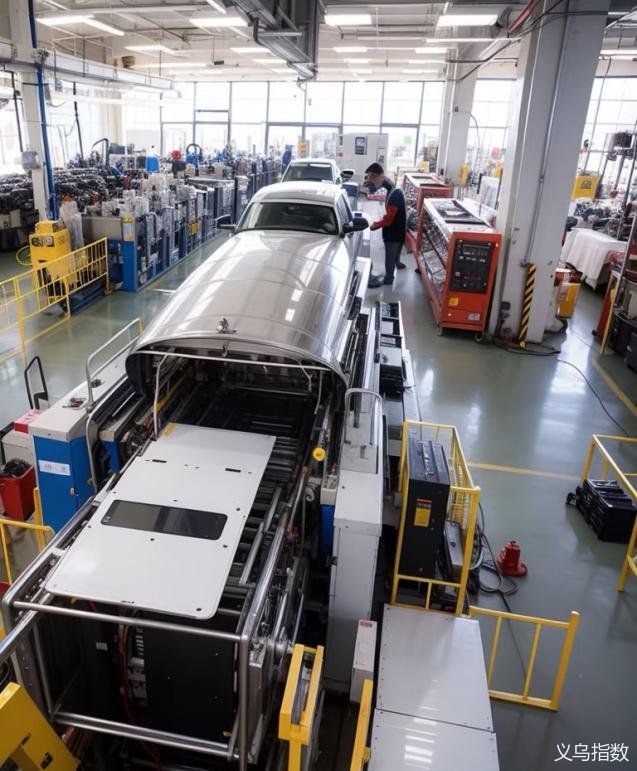

Image source: Yiwu Index
Mexico's light industry mainly focuses on traditional sectors such as textiles, food, cigarettes, papermaking, and leather tanning. It generally suffers from slow technological iteration, weak industrial chain integration capabilities, and low product added value, making it difficult to fully meet the diverse and high-quality domestic consumption demands. Therefore, Mexico is highly dependent on imports for small commodities, among which China is its main supplier.
Meanwhile, although agriculture has been impacted by genetically modified agricultural products from the United States, it has a rich variety of cash crops, including tomatoes, soybeans, sisal, tequila, etc. Among them, the export volume of tequila ranks first in the world. Since 2019, agricultural product exports have surpassed oil, tourism and remittances from overseas Chinese to become a key source of foreign exchange, and China is the largest export market for Mexican agricultural products.

Montana tequila in northern Mexico. Image source: Internet
This leaves Mexico's economic development with only two key words: the first is the United States, and the second is China.
02
Too far from heaven, too close to the United States
(1) Geographical proximity
The long border: The United States and Mexico have been neighbors for hundreds of years. Mexico shares a border with the United States, which is 3,145 kilometers long and is one of the longest land borders in the world. This border line extends from the Gulf of Mexico to the Pacific Ocean, with a complex geographical environment that includes deserts, rivers and urban areas, making the implementation of border patrols and security measures even more difficult.

The source of the US-Mexico border map: Xinhua News Agency
Faster logistics channels and higher efficiency: The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) has further simplified customs procedures, enhancing customs clearance efficiency. In terms of land transportation: Taking the Laredo Port in Texas as an example, it processes over 14,000 freight trucks on average each day. Goods can be directly transported to major inland cities in the United States by land within 24 to 48 hours. In terms of air transport, hub airports such as Mexico City and Monterrey operate over 200 cargo flights to the United States every day. High-efficiency goods like fresh produce and electronic products can be delivered directly within 6 to 8 hours. Sea transportation relies on Pacific ports such as the Port of Manzanillo, and the route to the Port of Los Angeles only takes 3 to 5 days.

Image source: Internet
(2) "The US economy has a cold, while Mexico's economy has pneumonia."
The United States is Mexico's largest "financial backer". Mexico's economy is highly dependent on the US market, and in its export structure, the United States is Mexico's largest trading partner.
The largest trading partner: According to data from the Central Bank of Mexico, Mexico's exports to the United States have risen overall since 2017, from 326.86 billion US dollars in 2017 to 506 billion US dollars in 2024, an increase of 54.8%. In terms of share, the proportion of exports to the United States in Mexico's total exports rose from 79.83% in 2017 to 82% in 2024. In 2023, Mexico had already surpassed China to become the largest source of imports for the United States.
The largest source of foreign investment: According to historical data, since the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) came into effect in 1994, US investment in Mexico has continued to grow. The United States is not only Mexico's largest trading partner but also its largest source of foreign investment. Its investment is mainly concentrated in manufacturing, finance, energy and infrastructure and other fields.
Proportion of foreign direct investment (FDI) attracted by Mexico in 2024 (%)
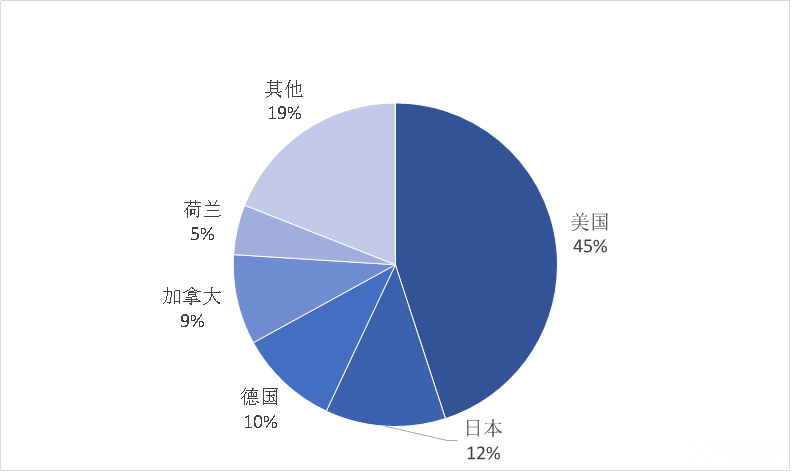
Data source: El Pais Mexico Edition of Spain
www.ywindex.com
"The US economy has a cold, while Mexico has pneumonia." Just as two sides of the same coin, this deep dependence makes Mexico's economy even more vulnerable, which is precisely the root cause of being "too far from heaven".
03
China: An "Economic Tango" Spanning the Pacific
China is Mexico's second-largest trading partner, second only to the United States. Mexico's imports from China have been steadily rising, reaching 14.42% of its total imports in 2024.
China-mexico relations
The "Chinese core" behind "Made in Mexico" : Mexico mainly imports technology-intensive and capital-intensive products such as electronic components and auto parts from China. Among them, 70% of the Asian imported goods (mainly Chinese components) are purchased by foreign companies in Mexico (such as American automotive and semiconductor enterprises) for processing and then exported to the United States. For instance, in the electronic products and automobiles assembled in Mexico, core components such as display screens and batteries are mostly sourced from China, forming a trade model of "Made in Mexico, with Chinese chips". Mexico mainly exports crude oil, agricultural products and other goods to China.
The proportion of the top ten Chinese export commodities in Mexico's imports (Unit: %)
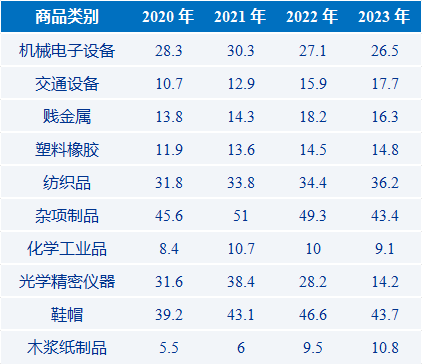
Data source: BACI, Yiwu Index
www.ywindex.com
The overall scale has continued to grow, with a good growth trend in recent years: The trade volume between Mexico and China has been increasing, from 60.846 billion US dollars in 2020 to 109.426 billion US dollars in 2024, an increase of 79.84%. Among them, in 2024, China's export volume to Mexico was 90.232 billion US dollars, and its import volume was 19.195 billion US dollars.
Changes in China's Export Trade Volume with Mexico from 2020 to 2024 (Unit: billion US dollars)
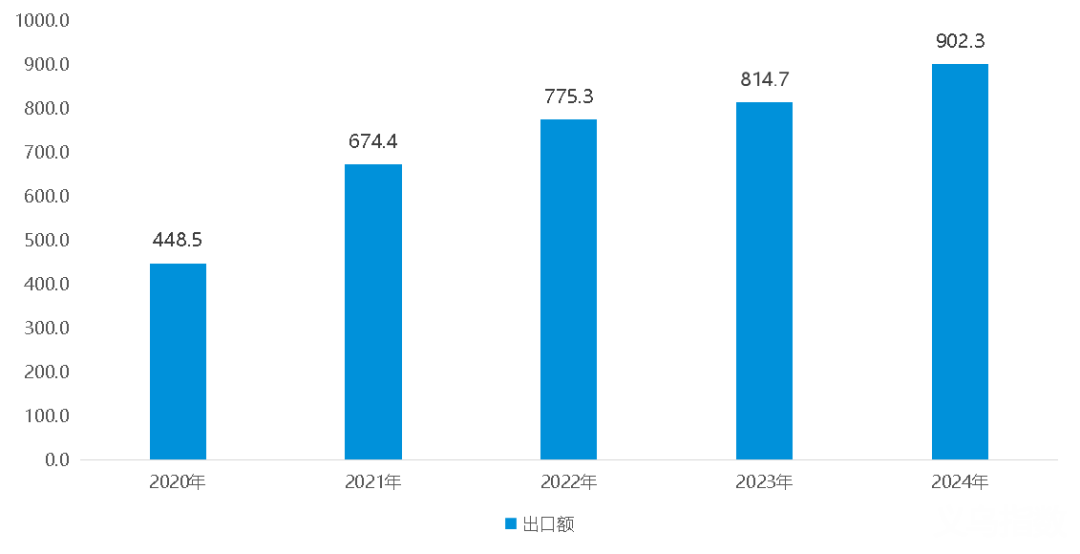
Data source: Chinese Customs
www.ywindex.com
The trade surplus is obvious: China has maintained a large trade surplus with Mexico for a long time. From 2020 to 2024, China achieved a cumulative trade surplus of 271 billion US dollars with Mexico. The average annual trade surplus over the past five years was 53.1 billion US dollars, and the trade surplus in 2024 was 71.037 billion US dollars.
China's trade surplus with Mexico from 2020 to 2024 (unit: billion US dollars)
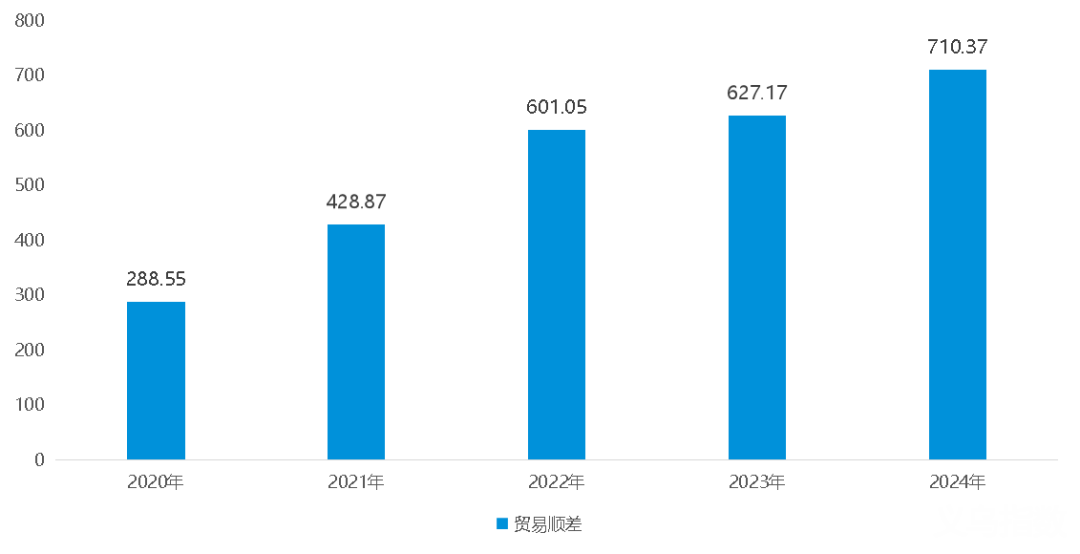
Data source: Chinese Customs
www.ywindex.com
(2) Yiwu is making efforts in small commodity trade
The Mexican market is increasingly dependent on Chinese small commodities. With significant price and quality advantages, Chinese goods, especially electronic products, toys, clothing, household items and other categories, are widely popular and dominant in Mexico.
As a core trade hub for small commodities in China, Yiwu plays a key role in exports to Mexico. A typical example is that among the Christmas decorations imported from Mexico, up to 70% come from China, covering all categories from colored lights to resin sculptures. The Yiwu market holds an absolute dominant position in Christmas products.
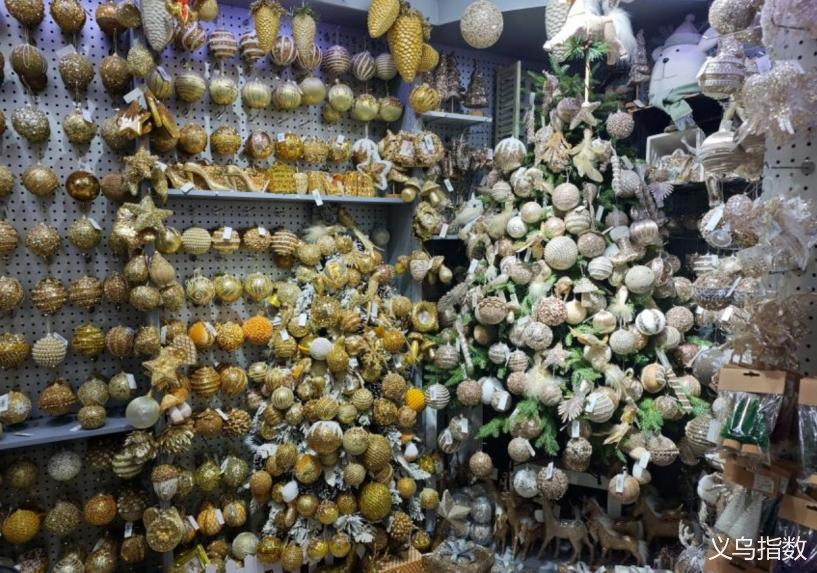

The Christmas ornaments operated by merchants in Zone 1 of Yiwu International Trade City. Source: Yiwu Index
According to the monitoring of Yiwu Index, from January to May 2025. Yiwu's export volume to Mexico reached 8.968 billion yuan, ranking fourth after the United States, India and Brazil. Over the past three years, Yiwu's export volume to Mexico has maintained a high growth rate. In 2024, Yiwu's export volume to Mexico exceeded 24 billion yuan, representing a year-on-year increase of 19.5%. In 2023, Yiwu's export volume to Mexico reached 20.094 billion yuan, representing a year-on-year growth of 42.5%. The top five categories of products exported from Yiwu to Mexico are: plastic products, toys, furniture, electronic products, beauty and personal care products, etc.
Yiwu's export volume to Mexico from 2022 to 2024 (Unit: 100 million RMB)
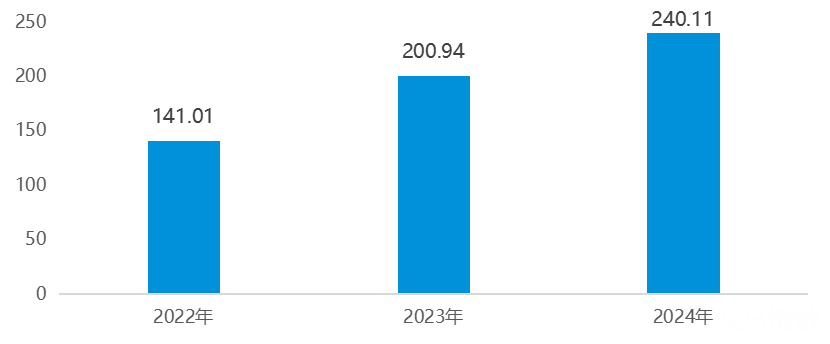
Data source: Yiwu Index
www.ywindex.com
04
The two sides of Mexico
Just like the two sides of a coin, the prosperous Mexican market also has a dark side:
Safety is the "admission ticket" : The security situation in Mexico is an unavoidable hard threshold for enterprises to enter its market. Some areas can be regarded as "minefields", with a high incidence of drug trafficking syndicates and violent crimes. Enterprises should avoid such high-risk zones. Especially, goods during transportation are constantly at risk of robbery or theft.
Tariffs are prone to change: As a member of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), Mexico's tariff policies are often adjusted under pressure from the United States, which often affects the export of Chinese goods. For instance, Mexico raised its most-favored-nation (MFN) tariffs twice, in August 2023 and April 2024. The tariffs mainly covered 544 items including steel, textiles, clothing, footwear, and plastics, with rates ranging from 5% to 50%. The scope of taxation included Chinese goods, but also affected those from third countries such as Brazil, South Korea, or Turkey.
High credit risk: Chinese exporters trading with Mexico need to be vigilant about the payment credit risk of their counterparties. Although Mexico has a relatively complete legal framework, the efficiency of judicial enforcement is generally low. When dealing with contract disputes and debt recovery, enterprises often encounter the challenges of lengthy procedures and high costs, and the process of collecting payments may consume a great deal of time and resources.
The risk of payment status of Mexican enterprises in the past year
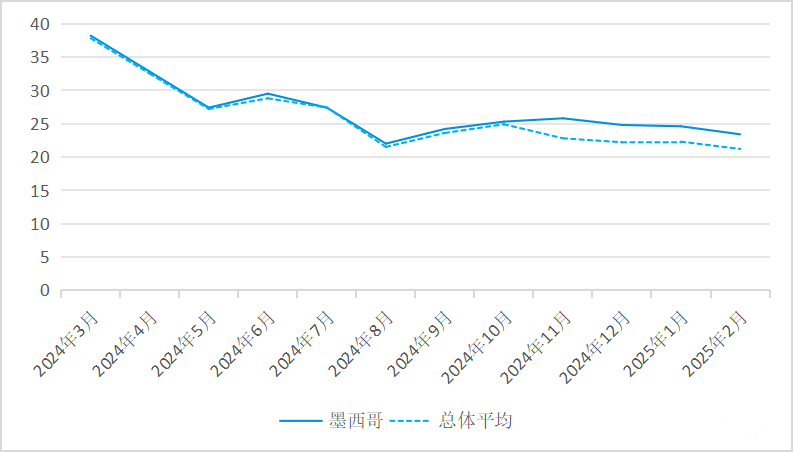
Data source: China Export & Credit Insurance Corporation Enterprise Services
www.ywindex.com
The uncertainty in Sino-US trade will cause this pressure to be passed on to China and Mexico. However, Mexico is an indispensable and crucial hub in the foreign trade between China and the United States, which is determined by its geographical location. For China, Mexico is a key alternative source of American agricultural products. For the United States, Mexico is an important alternative supply base for Chinese manufacturing. For the trade of small commodities, Mexico's vast market, dense population and strong demand all make it an important market for the export of small commodities.
—— The content of this article is translated by Al ——


 My favorites
My favorites